dbos.dev
DBOS simplifies building reliable and observable programs. Add a few annotations to your code to make it resilient to any failure.
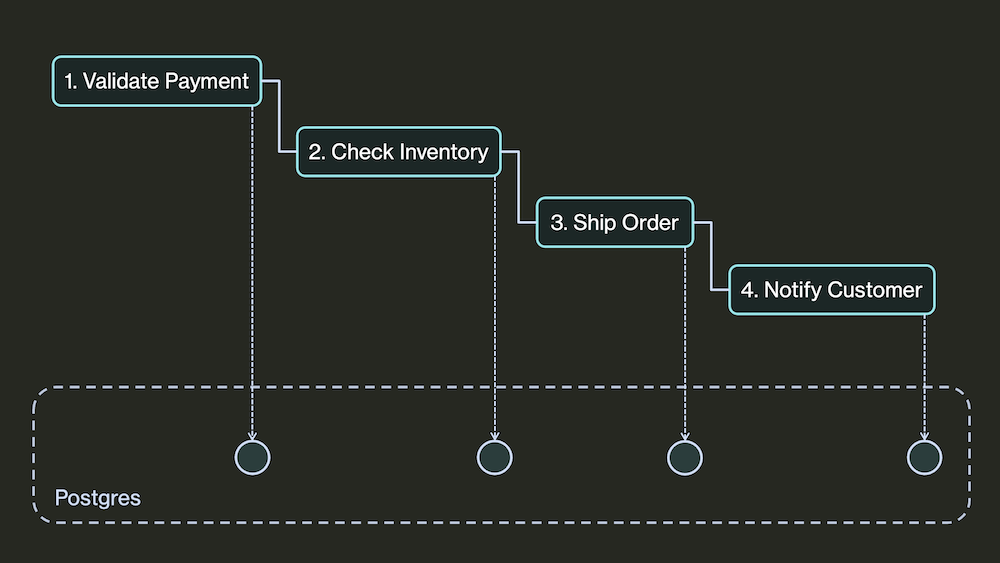
business logic in normal code, with branches, loops, subtasks, and retries. DBOS makes it resilient to any failure.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def validate_payment():
...
def checkout_workflow()
validate_payment()
check_inventory()
ship_order()
notify_customer()Launch any task to run in the background and guarantee it eventually completes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
def schedule_reminder(to_email, days_to_wait):
DBOS.recv(days_to_seconds(days_to_wait))
send_reminder_email(to_email, days_to_wait)
def email_endpoint(request):
DBOS.start_workflow(schedule_reminder, request.email, request.days)Schedule functions to run at specific times.
1
2
3
4
5
6
def run_hourly(scheduled_time, actual_time):
results = search_hackernews("serverless")
for comment, url in results:
post_to_slack(comment, url)Build data pipelines that are reliable and observable by default. DBOS durable queues guarantee all your tasks complete.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8queue = Queue("indexing_queue")
def indexing_workflow(urls):
handles = []
for url in urls:
handles.append(queue.enqueue(index_step, url))
return [h.get_result() for h in handles]Consume Kafka messages exactly-once, no need to worry about timeouts or offsets.
1
2
3
4
5
6
def process_kafka_alerts(msg):
alerts = msg.value.decode()
for alert in alerts:
respond_to_alert(alert)Use durable workflows to build reliable, fault-tolerant AI agents. Integrate with popular frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def agentic_research_workflow(topic, max_iterations):
research_results = []
for i in range(max_iterations):
research_result = research_query(topic)
research_results.append(research_result)
if not should_continue(research_results):
break
topic = generate_next_topic(topic, research_results)
return synthesize_research_report(research_results)
def research_query(topic):
...
在金融系统中的优势分析:
- 天然适合银行交易场景:DBOS的工作流模式完美匹配银行的多步骤交易处理需求
- PostgreSQL基础:许多银行已经在使用PostgreSQL,技术栈融合度高
- 故障恢复能力:关键业务操作的自动恢复功能对银行至关重要
- 代码简洁性:通过注解方式实现持久化,降低开发复杂度
潜在挑战:
- 监管合规:需要验证DBOS是否满足银行业的严格审计要求
- 性能要求:大型银行的高并发交易处理能力需要充分测试
- 企业集成:与现有核心银行系统的集成复杂性
- 安全标准:是否符合PCI-DSS、SOX等金融行业安全标准
1 | // case 1:客户服务流程 |
DBOS实际上是多种设计模式的巧妙组合:
- 责任链模式 (Chain of Responsibility)
1 | // 经典责任链:每个处理器处理请求或传递给下一个 |
- Saga模式 (最核心的模式)
这是DBOS最准确的模式匹配:
1 | // Saga模式:长事务的分解与补偿 |
命令模式 + 备忘录模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7// 每个步骤都是可存储和重放的命令
.step()
async function executePayment(payment: Payment) {
// DBOS在PostgreSQL中存储此步骤的状态
// 失败时可从此检查点重放
return await processPayment(payment);
}状态机模式
1 | // 银行交易状态机 |
- Oracle Database - transaction procedure
核心相似性分析
事务边界管理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8-- Oracle: 显式事务控制
BEGIN
SAVEPOINT sp1;
-- operations
COMMIT;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN ROLLBACK TO sp1;
END;状态持久化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7-- Oracle: 数据库状态 + 过程状态
CREATE TABLE workflow_state (
workflow_id NUMBER,
step_name VARCHAR2(100),
step_status VARCHAR2(20),
step_data CLOB
);错误处理与补偿
1
2
3
4
5
6
7-- Oracle: 异常处理
EXCEPTION
WHEN custom_exception THEN
-- 补偿逻辑
ROLLBACK TO savepoint;
-- 清理操作
END;批处理与队列处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10-- Oracle: 批处理存储过程
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE PROCESS_DAILY_BATCH AS
CURSOR c_transactions IS
SELECT * FROM pending_transactions;
BEGIN
FOR rec IN c_transactions LOOP
PROCESS_SINGLE_TRANSACTION(rec.txn_id);
END LOOP;
COMMIT;
END;
模式对比表
| 特性 | Oracle存储过程 | DBOS工作流 |
|---|---|---|
| 事务边界 | BEGIN/COMMIT/ROLLBACK | @DBOS.workflow() |
| 步骤控制 | 嵌套BEGIN块 | @DBOS.step() |
| 状态保存 | SAVEPOINT | 自动检查点 |
| 错误恢复 | EXCEPTION处理 | 自动重启恢复 |
| 数据持久化 | Oracle表空间 | PostgreSQL |
| 并发控制 | FOR UPDATE锁 | PostgreSQL锁 |
| DBOS的现代化改进: |
- 分布式执行能力
- 自动故障恢复
- 云原生架构友好
- 更简洁的错误处理